Windows 10 Nfs Client
Description The Set-NfsClientConfiguration cmdlet changes configuration settings for a Network File System (NFS) client. You can use the Get-NfsClientConfiguration cmdlet to get a configuration object for an NFS client. We had two NFS shares that we needed to allow windows user's to connect (if it was possible) after some hassle it was. This is specifically for a machine that is not on an active directory domain or if you do not want to set up the AD identity service. I have tested this functionality in Windows 7 SP1, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10 Anniversary.
Concept
I wanted to have my virtualization servers NFS shared storage pool accessible by my Windows 10 system.
However, it seems that the only way to mount an NSF share to windows is to manually enter the command once logged in. When the PC restarts, the drive is no longer mounted.
This guide will show you how to get it setup and have it persist on restarts.
Dependencies
- Windows 10 Pro or higher
- NFS server accessible on your local network
Disclaimers: Not guaranteed to work on a system with multiple active users or a NFS server without a static IP.
Install the NFS Client
- Go to Control Panel > Programs and Features > Turn Windows Features on or off
- Enable “Services for NFS” with both subcategories
Enable Write Permission for the Anonymous User
- Go to Regedit >
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftClientForNFSCurrentVersionDefault - Create a new New DWORD (32-bit) Value inside the Default folder named AnonymousUid and assign the UID found on the UNIX directory as shared by the NFS system (Default:
0) - Create a new New DWORD (32-bit) Value inside the Default folder named AnonymousGid and assign the GID found on the UNIX directory as shared by the NFS system (Default:
0) - Restart the PC to apply the changes
Mount the NFS Share
Open command prompt and enter the command below:
-o anonsets the user to anonymous<ip_address>/mnt/locationis the path to the NFS share on the NFS serverZ:is the drive that the NFS share will be mounted to on the Windows system
Setup Auto-Mount on Startup
Open the Startup folder by opening the Run tool and entering shell:startup
Create a nfsmount.bat file in that directory with the mount command used above.
This file will be read on startup and will automatically mount the NFS Share.
In this short guide I will talk about how to mount a shared drive that is in an Ubuntu or Debian installation that will be the server with the NFS (Network File System) drive, on a network drive accessible from Windows 10 who will play the role of client.
Table of Contents

- Installation and configuration in Ubuntu or Debian as a server
- Client installation and configuration in Windows 10
 ⇧
⇧1. Installation and configuration in Ubuntu or Debian as a server
In the case of Debian, remove sudo in each command (it can even be executed the same).
Install the package 'nfs-kernel-server':
1.1. Drive options
Then we edit the file /etc/exports with nano or with the editor of our preference:
The file contains comments such as the following:
We add a line at the end with the following:
In the example above:
/home/user/folder it is the folder that will be shared by the network.
192.168.0.10 it is the IP of the client or clients that access the network resource. Only a static IP is shown, but we can use 192.168.0.1/24 to match between 192.168.0.1 and 192.168.0.254.
Mount options are in parentheses.
Windows 10 Nfs Client Home
- rw: allow reading and writing.
- sync: is optional in case we want a little more file integrity and avoid data loss, sacrificing a bit of performance.
- all_squash: downgrades the permissions of the files created from the client to the nobody user. For example, if in Windows 10 I am logged in as Administrator and created a new file, it will belong to user nobody.
- anonuid: is the ID of the nobody user, or whatever user we want.
- anongid: is The group ID of the user nobody.
In this case I set anonuid and anongid to 1000, which is the user who owns the folder, /home/user/folder to preserve execute and write permissions.
With the changes made we save the file CTRL + O, then Enter, and then we close with CTRL + X, this only if we use the nano editor from the terminal.
We restart the NFS server:
With this, the configuration on the server will be ready, any error that appears when restarting is necessary to check the configuration and obviously the description of the error.
⇧2. Client installation and configuration in Windows 10
Windows comes with a default client, but it needs to be installed, the only detail is that I don't remember if it is available in the Windows 10 Home version.
The easiest way to install it is to use the search bar and type Control Panel, because Windows 10 has several modern panels that hide the older options. Open Programs › Programs and Features and in the left panel we open Turn Windows features on or off.
Mark the box Service for NFS with his two descendants Client for NFS and Administrative Tools. We click on OK and after some time the client will be installed.
2.1. Mounting the network drive
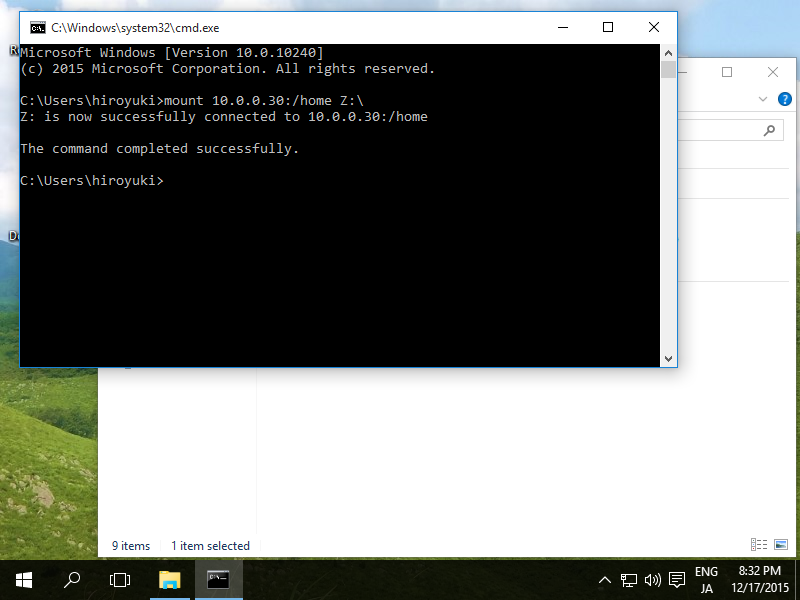
To mount the unit, we open the cmd (do not use PowerShell). We use the command:
The IP 192.168.0.20 is the server, followed by the shared folder and one drive letter that will be used. It is important to use the real full path of the resource as if we were personally on the server with the folder /home/user/folder, otherwise it won't work. I have tried hiding the part of the path when mounting the drive, but it is a complicated process and not worth the extra effort.
The message, The command completed successfully. will indicate that everything is working properly.
Windows 10 Nfs Client Free
2.2. Write permissions for the anonymous user
Normally and by default, Windows does not allow writing to this type of drives with the anonymous user. To enable writing, we have to open the Windows registry Regedit, and we headed towards: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftClientForNFSCurrentVersionDefault.
There we will create a DWORD (32-bit) Value with the name AnonymousUid with the value of 0 with Base Decimal. Then create a DWORD (32-bit) Value with the name AnonymousGid with the value 0 with Base Decimal.
We have to restart the computer or the service Client for NFS, we can find it in the task manager in the Services tab.
If we follow all the previous steps, and we already have the unit mounted, we open the CMD and execute the command mount, the mount will appear and in properties it will show UID=0 y GID=0. If any other number appears, check the entire procedure above.

Notes: The procedure is practically the same in both Ubuntu and Debian, or any other variation like Kubuntu. No need to use Ubuntu Server. The NFS version to be used is 3 with Ubuntu 18.04 - 64-bits and Windows 10.
⇧