Therm Software
The therm (symbol, thm) is a non-SIunit of heatenergy equal to 100,000 British thermal units (Btu[1]). It is approximately the energy equivalent of burning 100 cubic feet (2.83 cubic metres) – often referred to as 1 CCF – of natural gas.
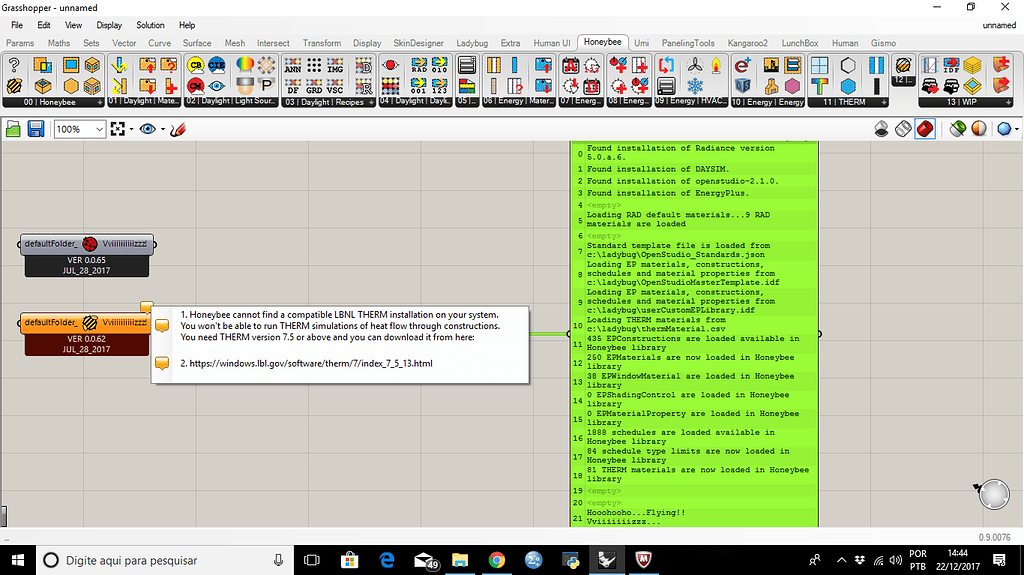
Jul 13, 2021 THERM is a state-of-the-art, Microsoft Windows™-based computer program developed at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) for use by building component manufacturers, engineers, educators, students, architects, and others interested in heat transfer. Jul 07, 2010 When you install this new version of THERM, a completely new set of directories is created, so that you can have other versions (THERM 7.4 and 7.6) installed at the same time. Redistributable Packages/Libraries that MUST BE installed before this version will run (if they have not been previously installed). In this video you will learn how to download and install therm on your windows machine.
Since natural gas meters measure volume and not energy content, a therm factor is used by natural gas companies to convert the volume of gas used to its heat equivalent, and thus calculate the actual energy use. The therm factor is usually expressed in units of therms per CCF. It will vary with the mix of hydrocarbons in the natural gas. Natural gas with a higher than average concentration of ethane, propane or butane will have a higher therm factor. Impurities, such as carbon dioxide or nitrogen, lower the therm factor.
The volume of the gas is calculated as if measured at standard temperature and pressure (STP).
One therm is equal to about 105.5megajoules, 25200kilocalories, or 29.3kilowatt-hours.
The therm sometimes has been confused with the thermie. The names of both units come from the Greek word for heat.
Definitions[edit]
Therm Software For Mac
- Therm (EC) ≡ 100000BTUISO[2]
- = 105506000joules
- ≈ 29.3072kWh
- The therm (EC) is often used by engineers in the US.
- Therm (US) ≡ 100000BTU59°F[3]
- = 105480400joules
- ≈ 29.3001111111111kWh.
- Therm (UK) ≡ 105505585.257348joules[4]
- ≡ 29.3071070159300kWh
10 therms are known as a decatherm (sometimes, dekatherm;[5] commonly abbreviated Dth), which is 1000000Btu (of whichever type). Further common abbreviations are MDth for a 1000 decatherms, and MMDth for 1000000 decatherms.[5][failed verification]
Usage[edit]
United Kingdom regulations were amended to replace therms with joules with effect from 1999, with natural gas usually retailed in the derived unit, kilowatt-hours. Despite this, the wholesale UK gas market trades in therms. In the United States, natural gas is commonly billed in CCFs (hundreds of cubic feet) or therms.
Carbon footprint[edit]
Therm Software Rittal
According to the EPA burning one therm of natural gas produces on average 5.3 kg (11.7 lb) of carbon dioxide.[6]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^IEEE Std 260.1-2004
- ^Official Journal L 073, P. 0114 27 March 1972
- ^15 USC Chapter 6Archived 2006-01-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^The Units of Measurement Regulations 1995
- ^ abJerry Knight (22 January 1978). 'Gas Utilities Stepping Up Efforts to Add Customers'. The Washington Post. Retrieved 1 June 2016.
- ^epa.gov 'Greenhouse Gases Equivalencies Calculator - Calculations and References
The therm (symbol, thm) is a non-SIunit of heatenergy equal to 100,000 British thermal units (Btu[1]). It is approximately the energy equivalent of burning 100 cubic feet (2.83 cubic metres) – often referred to as 1 CCF – of natural gas.
Since natural gas meters measure volume and not energy content, a therm factor is used by natural gas companies to convert the volume of gas used to its heat equivalent, and thus calculate the actual energy use. The therm factor is usually expressed in units of therms per CCF. It will vary with the mix of hydrocarbons in the natural gas. Natural gas with a higher than average concentration of ethane, propane or butane will have a higher therm factor. Impurities, such as carbon dioxide or nitrogen, lower the therm factor.
The volume of the gas is calculated as if measured at standard temperature and pressure (STP).
One therm is equal to about 105.5megajoules, 25200kilocalories, or 29.3kilowatt-hours.

The therm sometimes has been confused with the thermie. The names of both units come from the Greek word for heat.
Definitions[edit]
- Therm (EC) ≡ 100000BTUISO[2]
- = 105506000joules
- ≈ 29.3072kWh
- The therm (EC) is often used by engineers in the US.
- Therm (US) ≡ 100000BTU59°F[3]
- = 105480400joules
- ≈ 29.3001111111111kWh.
- Therm (UK) ≡ 105505585.257348joules[4]
- ≡ 29.3071070159300kWh
Therm Software Not Responding
10 therms are known as a decatherm (sometimes, dekatherm;[5] commonly abbreviated Dth), which is 1000000Btu (of whichever type). Further common abbreviations are MDth for a 1000 decatherms, and MMDth for 1000000 decatherms.[5][failed verification]
Usage[edit]
United Kingdom regulations were amended to replace therms with joules with effect from 1999, with natural gas usually retailed in the derived unit, kilowatt-hours. Despite this, the wholesale UK gas market trades in therms. In the United States, natural gas is commonly billed in CCFs (hundreds of cubic feet) or therms.

Carbon footprint[edit]
According to the EPA burning one therm of natural gas produces on average 5.3 kg (11.7 lb) of carbon dioxide.[6]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Therm Software 7.5 Tutorial
- ^IEEE Std 260.1-2004
- ^Official Journal L 073, P. 0114 27 March 1972
- ^15 USC Chapter 6Archived 2006-01-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^The Units of Measurement Regulations 1995
- ^ abJerry Knight (22 January 1978). 'Gas Utilities Stepping Up Efforts to Add Customers'. The Washington Post. Retrieved 1 June 2016.
- ^epa.gov 'Greenhouse Gases Equivalencies Calculator - Calculations and References